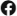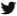KHAN YOUNIS, Gaza Strip (AP) — Two years ago, Sarah Qanan was a star high school student preparing for final exams and dreaming of becoming a doctor. Today, the 18-year-old lives in a sweltering tent in the Gaza Strip and says she is just trying to stay alive.
She’s part of a generation of Palestinians from grade school through university who have had virtually no access to education in the territory since the war began in October 2023. Classes were suspended that month and schools were transformed into crowded shelters as hundreds of thousands fled their homes at the start of Israel’s campaign of retaliation after Hamas’ Oct. 7, 2023, attack.
The closure of schools has removed a key social outlet for young people as they grapple with war, hunger and displacement. For younger children, it has meant missing out on basic skills like reading and simple arithmetic. For older students, advanced subjects, graduation exams and college applications have all been put on hold.
Even if negotiations lead to another ceasefire, it’s unclear when anything in Gaza will be rebuilt. Vast areas have been completely destroyed, and the U.N. children’s agency estimates that nearly 90% of schools will need substantial reconstruction before they can function again.
Like many in Gaza, Qanan’s family has been displaced multiple times and is now living in a tent. When an Israeli airstrike destroyed their home in early 2024, she dug through the rubble in search of her books, but “there was nothing left.”

Sarah Qanan studies inside her family’s tent in Khan Younis, Gaza Strip, on June 28, 2025. (AP Photo/Abdel Kareem Hana)
“My sole dream was to study medicine,” Qanan said. “I stopped thinking about it. All my thoughts now are about how to survive.”
Hundreds of thousands out of school
More than 650,000 students have had no access to education since the start of the war, according to the U.N. children’s agency, UNICEF. That includes nearly 40,000 students who were unable to take university entry exams that largely determine their career prospects.
It’s the first time in decades that the exams were not administered in Gaza.
Israel’s bombardment and ground operations have killed tens of thousands of Palestinians and displaced 90% of Gaza’s population. School-age children in crowded shelters and tent camps are often forced to help their families find food, water and firewood. A complete Israeli blockade imposed in early March that was only slightly eased 2 ½ months later has driven the territory to the brink of famine.
Local education officials, working with UNICEF and other aid groups, set up hundreds of learning spaces to try and provide education during the war.
“We’re trying to salvage what we can of the educational process, so that the next generation doesn’t slip through our fingers,” said Mohamed al-Asouli, head of the education department in the southern city of Khan Younis.

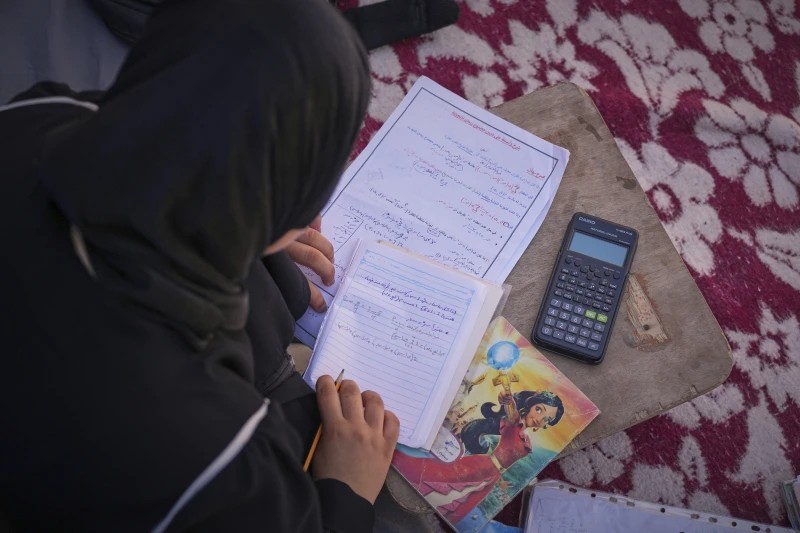
Displaced Palestinians live in a school run by UNRWA, the U.N. agency, in Gaza City, Monday, June 23, 2025. (AP Photo/Jehad Alshrafi, File)
During a six-week ceasefire in January and February, some 600 learning spaces provided lessons for around 173,000 children, according to UNICEF. But since March, when Israel ended the truce with a surprise bombardment, nearly half have shut down.
“The impact goes beyond learning losses,” said Rosalia Bollen, a UNICEF spokeswoman. “Children in Gaza have been trapped in a cycle not just of exposure to unprecedented violence, but also a cycle of fear, of toxic stress, of anxiety.”
‘Two years of my life are gone’
Some have tried to continue their studies through online learning, but it’s not easy in Gaza, where there has been no central electricity since the start of the war. Palestinians must use solar panels or hard-to-find generators to charge their phones, and internet is unreliable.
“The mobile phone is not always charged, and we only have one at home,” said Nesma Zouaroub, a mother of four school-age children. She said her youngest son should be in second grade but does not know how to read or write.
“The children’s future is ruined,” she said.
Ola Shaban tried to continue her civil engineering studies online through her university after the campus was destroyed by Israeli forces in April 2024. She had to walk long distances to get a signal in her hometown near Khan Younis, and she eventually gave up.
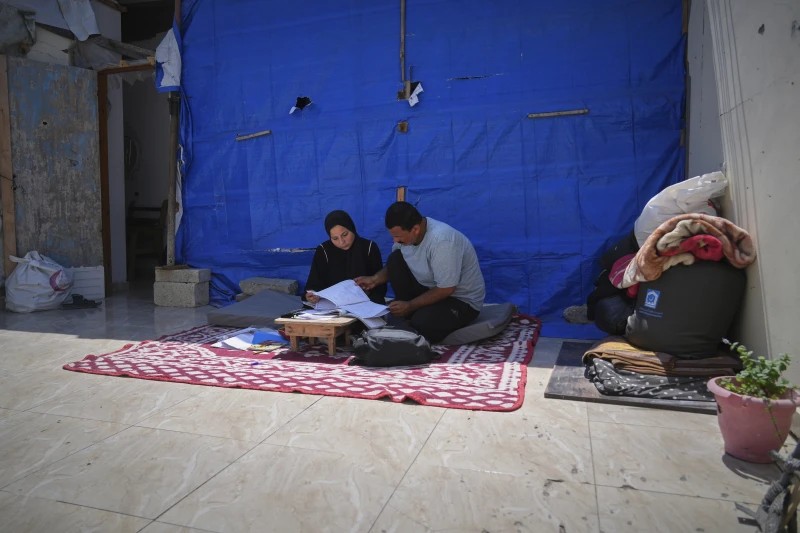

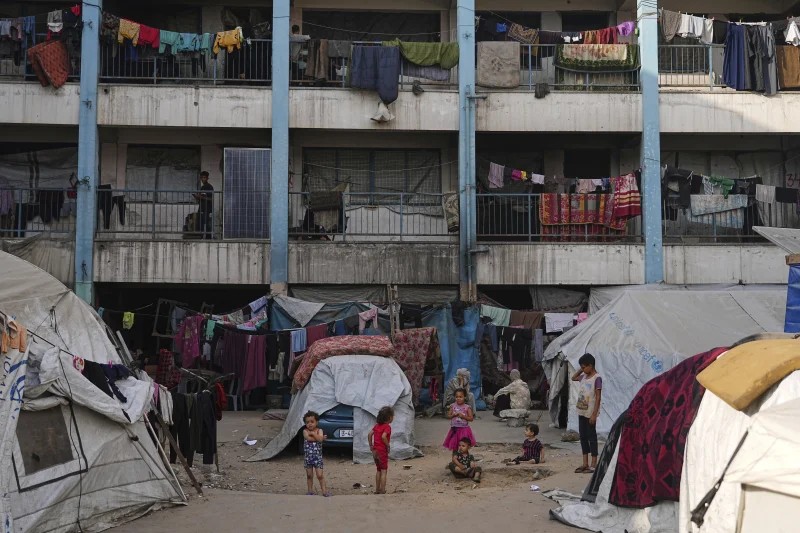
Sarah Qanan studies with her father, Ibrahim, in their family’s tent in Khan Younis, Gaza Strip, on June 28, 2025. (AP Photo/Abdel Kareem Hana)
“I couldn’t continue because of lack of internet, continuous displacement and the constant sense of fear,” she said. “Two years of my life are gone.”
Israel’s offensive has killed over 57,000 Palestinians, according to Gaza’s Health Ministry. The ministry, which is part of the Hamas-run government, does not differentiate between combatants and civilians but says over half the dead are women and children. Its figures are used by the U.N. and other international organizations as the most reliable statistics on war casualties.
Hamas-led militants killed some 1,200 people in the Oct. 7 attack and abducted 251. They are still holding 50 hostages, less than half believed to be alive, after most of the rest were released in ceasefire deals or other agreements.
Qanan’s father, Ibrahim, a local journalist, said his family did everything it could to support Sarah’s ambition to study medicine, only to see it go up in smoke when the war broke out.
“The war stunned us and turned our life upside down,” the father of six said. “Our dreams and hopes were buried in the rubble of our home.”